Acid-base reactions are some of the most important and common reactions in chemistry and are essential for everyday life. From the production of food and drink to the manufacture of medicines, these reactions are a fundamental part of our lives. But what exactly are acid-base reactions and how do they work? In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of acid-base reactions and discover the surprising power of the salt of weak acid and strong base!
Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. These reactions are an essential part of everyday life – from the production of food and drink to the manufacture of medicines, these reactions are a fundamental part of our lives. But what are they and how do they work? In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of acid-base reactions and discover the surprising power of the salt of weak acid and strong base!
Acid-base reactions are an important part of chemistry, and understanding them is essential for many real-world applications. They are a type of chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. These reactions are an essential part of everyday life – from the production of food and drink to the manufacture of medicines, these reactions are a fundamental part of our lives. But what are they and how do they work? In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of acid-base reactions and discover the surprising power of the salt of weak acid and strong base!
What is an Acid-Base Reaction?
An acid-base reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. In this process, hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid react with hydroxide ions (OH-) from the base to form a salt and water. This reaction is also called a neutralization reaction, as the acid and base are neutralized to form a salt and water.
The acid and base used in an acid-base reaction can be either strong or weak. A strong acid is one that completely dissociates in water, releasing all of its H+ ions. A strong base is one that completely dissociates in water, releasing all of its OH- ions. Weak acids and bases, on the other hand, only partially dissociate in water, releasing only a small amount of their H+ or OH- ions.
Types of Acid-Base Reactions
There are three types of acid-base reactions: neutralization, titration, and precipitation. A neutralization reaction is a reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt and water. A titration is a process of adding a measured amount of a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration. A precipitation reaction is a reaction in which two insoluble compounds react to form a soluble product.
Acid-Base Reactions Formulas
The acid-base reaction formulas are used to calculate the amount of acid or base needed to neutralize a given amount of the other. The general formula for a neutralization reaction
is:- H+ + OH- → H2O + Salt
The amount of acid or base needed to neutralize a given amount of the other can be calculated using the following equation:
Moles of acid or base = moles of acid or base needed to neutralize
Where moles of acid or base = number of moles of acid or base present
Examples of Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are common in everyday life and can be seen in a wide range of situations. For example, when vinegar (an acid) is added to baking soda (a base), a neutralization reaction occurs, producing sodium acetate (a salt) and water. Another example is the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce sodium chloride (table salt) and water.
In addition, acid-base reactions are also used in the production of food and drink. For example, when an acidic food such as lemon juice is added to a basic food such as baking soda, a neutralization reaction occurs, producing carbon dioxide gas, which is responsible for the rise in dough when baking.
Acid-Base Reactions and pH
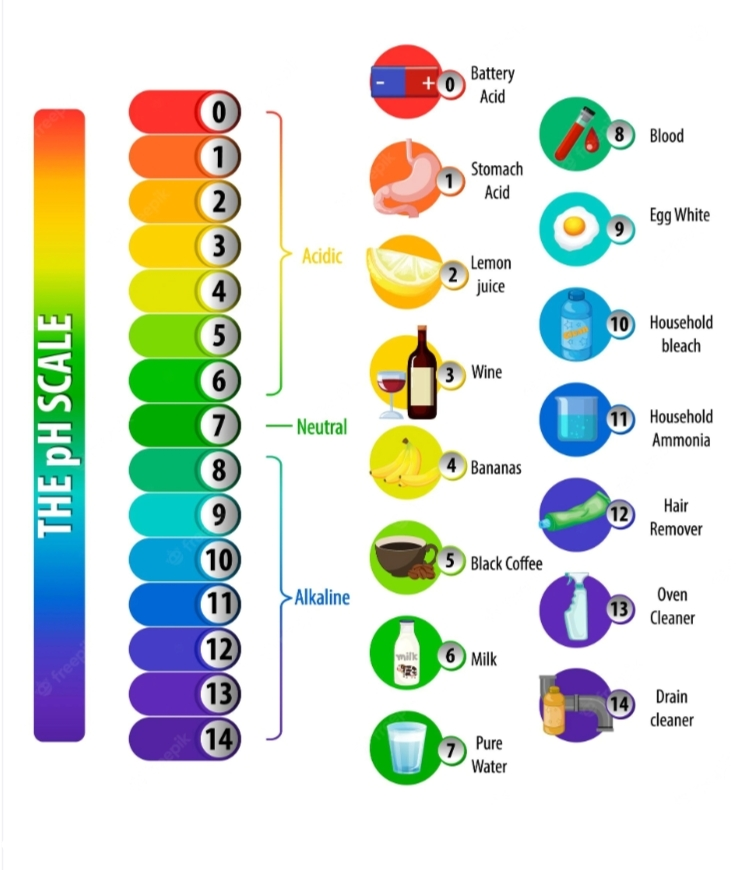
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic, 7 being neutral, and 14 being the most basic. An acid-base reaction affects the pH of a solution by either increasing or decreasing the number of H+ ions in the solution.
When an acid is added to a solution, the number of H+ ions increases, causing the pH to become more acidic. When a base is added to a solution, the number of H+ ions decreases, causing the pH to become more basic. This is why the pH of a solution can be used to determine whether a reaction is an acid-base reaction.
The Salt of Weak Acid and Strong Base
The salt of a weak acid and strong base is a compound formed when a weak acid and a strong base react together. This type of reaction produces a salt and water, but the salt formed is not the same as the salt formed in a neutralization reaction between a strong acid and a strong base. The salt formed from a weak acid and a strong base will be composed of the cation of the weak acid and the anion of the strong base.
For example, if acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) were to react, the salt formed would be sodium acetate (CH3COONa). In this reaction, the cation of the weak acid (the acetate ion, CH3COO-) is combined with the anion of the strong base (the sodium ion, Na+), forming the salt sodium acetate.
How to Write the Equations for Acid-Base Reactions
When writing equations for acid-base reactions, it is important to remember to include the phases. The phase of a reaction is whether the reactants and products are in aqueous (dissolved in water), solid, or gaseous form. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) react to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). The equation for this reaction would be written as follows:
HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
In this equation, the (aq) indicates that the reactants are in aqueous form, while the (l) indicates that the product (water) is in liquid form.
Acid-Base Reactions in Chemistry
Acid-base reactions are an important part of chemistry and are used in a wide range of applications. In organic chemistry, acid-base reactions are used to synthesize new compounds and to determine the structure of unknown compounds. In inorganic chemistry, they are used to identify metal ions and to predict the products of complex reactions.
For example, in a titration, a known volume of a solution of known concentration is added to a solution of unknown concentration. By measuring the volume of the titrant (the solution of known concentration) added to the sample solution, the concentration of the sample solution can be determined
Conclusion
In conclusion, acid-base reactions are essential for everyday life. From the production of food and drink to the manufacture of medicines, these reactions are a fundamental part of our lives. We have explored the fascinating world of acid-base reactions and discovered the surprising power of the salt of weak acid and strong base!
Acid-base reactions have many real-world applications, and understanding them is essential for many areas of chemistry.
